++ 50 ++ y=e^x transformations 948597-Y=e^x graph transformations
Consider the transformation of the natural exponential y = {eq}e^{x2} {/eq} 1 Describe the transformations in an appropriate orderExample 31 Find the rule of the image of f(x) under the following sequence of transformations A dilation from the xaxis by a factor of 3 A reflection in the yaxis A translation of 1 unit in the negative direction of the xaxisDescribe this transformation which maps y=e^x onto the graph of these functions 1 Y= e^3x 2 Y= e^x3 3 Y= lnx My solutions, which I am unsur

Which Transformations To The Graph Of Y Ex Would Result In The Graph Of Y Ex 34 Brainly Com
Y=e^x graph transformations
Y=e^x graph transformations-Graph y = e x;Graph y=e^ (x) y = e−x y = e x Exponential functions have a horizontal asymptote The equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 0 y = 0 Horizontal Asymptote y = 0 y = 0
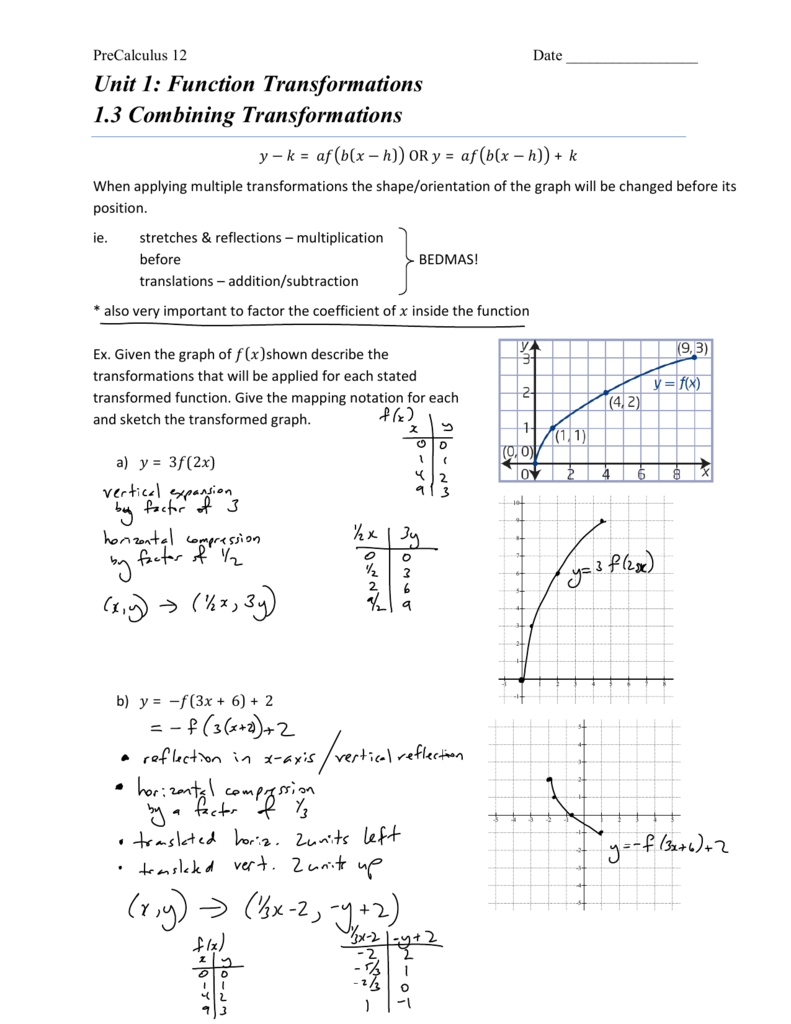



Unit 1 Function Transformations 1 3 Combining Transformations
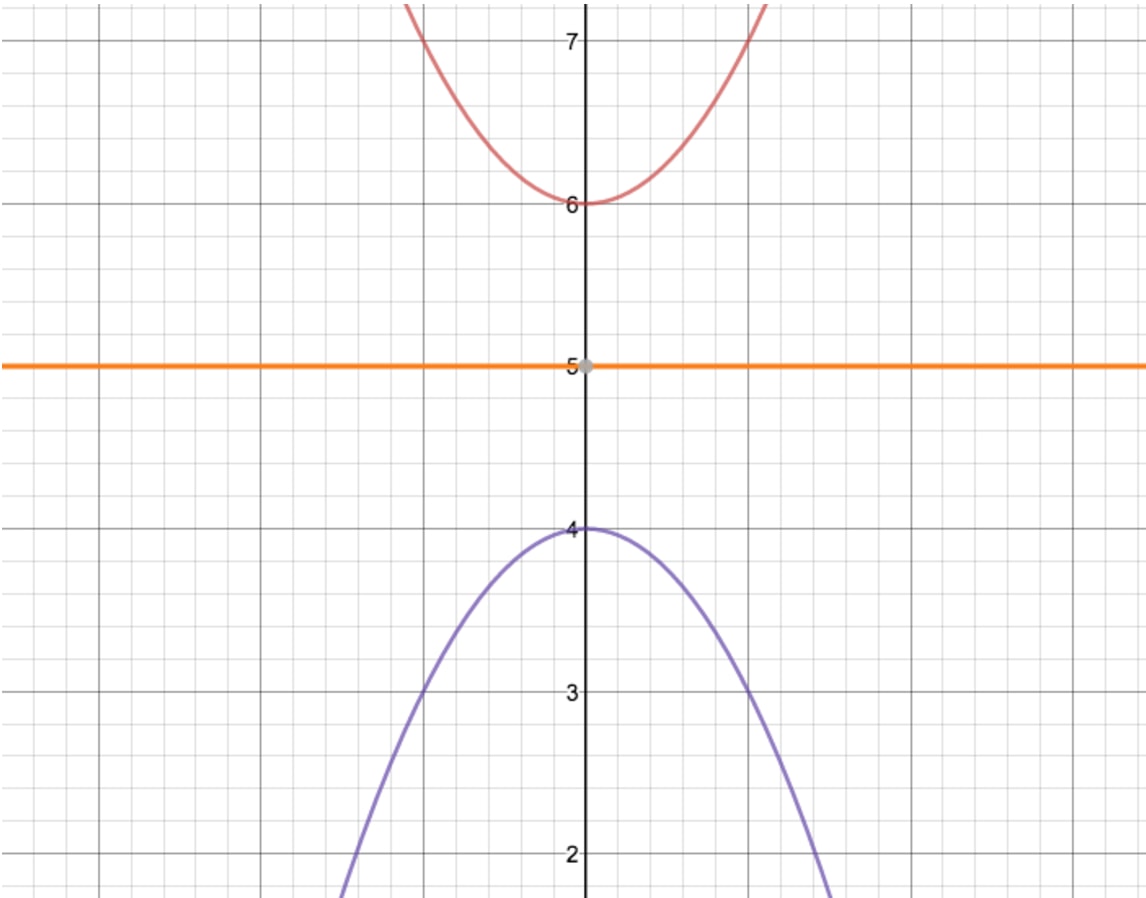
Move slider below to add more terms 3The mean, or first moment, of a distribution is a measure of the average Suppose that a random variable has three outcomes To calculate the mean of X, we compute E (X) That is, The variance of X is calculated as E (X X) 2 We can augment our table as follows Now, we take E (X X) 2 Suppose that the values of X were raised to 4, 6, and 13 Begin with the graph of y = e^x and use transformations to graph the function Determine the domain, range, and horizontal asymptote of the function f (x) = 2 e^(x/2)
Transformations of Exponential Functions Problem Using the enclosed Java applet, explore graphically the effect of changing the coefficients a, b, c, and d in the exponential function f (x) = a eb (x c) d Visualization f (x) = a eb (x c) d This exploration is about recognizing what happens to the graph of the exponential functionGraphing Reflections In addition to shifting, compressing, and stretching a graph, we can also reflect it about the xaxis or the yaxisWhen we multiply the parent function latexf\left(x\right)={b}^{x}/latex by –1, we get a reflection about the xaxisWhen we multiply the input by –1, we get a reflection about the yaxisFor example, if we begin by graphing the parentThis might feel a bit more difficult to graph, because just about all of my yvalues will be decimal approximationsBut if I round off to a reasonable number of decimal places (one or two is generally fine for the purposes of graphing), then this graph will be fairly easy
Thus, use of change of variables in a double integral requires the following 3 steps Find the pulback S in the new coordinate system (u,v) for the initial region of integration R;Transformations of Functions Practice STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by ccamathteach Terms in this set (44) horizontal shift to the left 1 unit horizontal shift to the right 2 units horizontal stretch byHere we discuss transformations involving two random variable 1, 2 The bivariate transformation is 1= 1( 1, 2) 2= 2( 1, 2) Assuming that 1 and 2 are jointly continuous random variables, we will discuss the onetoone transformation first Starting with the joint distribution of



Transforming Exponential Functions




Parent Functions And Transformations She Loves Math Math Lessons Teaching Algebra Math Methods
Transformations of Two Random Variables Problem (X;Y) is a bivariate rv Find the distribution of Z = g(X;Y) The very 1st step specify the support of Z X;Y are discrete { straightforward;3 The covariance of X and Y is defined as cov(X,Y) = E(X −µ X)(Y −µ Y) 4 The correlation (coefficient) of X and Y is defined as ρ XY = √ cov(X,Y ) var(X)var(Y ) The following properties about the variances are worth memorizing Theorem 4 (Variances and Covariances) Let X and Y be random variables and a,b ∈ R 1 var(aX bThis is the 3rd in a series of 3 tutorials where I show you how to sketch exponential graphs which are transformations of y = e x (stretching) Show Stepbystep Solutions Try the free Mathway calculator and problem solver below to practice various math topics Try the given examples, or type in your own problem and check your answer with the



Biomath Transformation Of Graphs



Expressing Transformatio Free Algebra 2 Worksheet Bakpax Bakpax
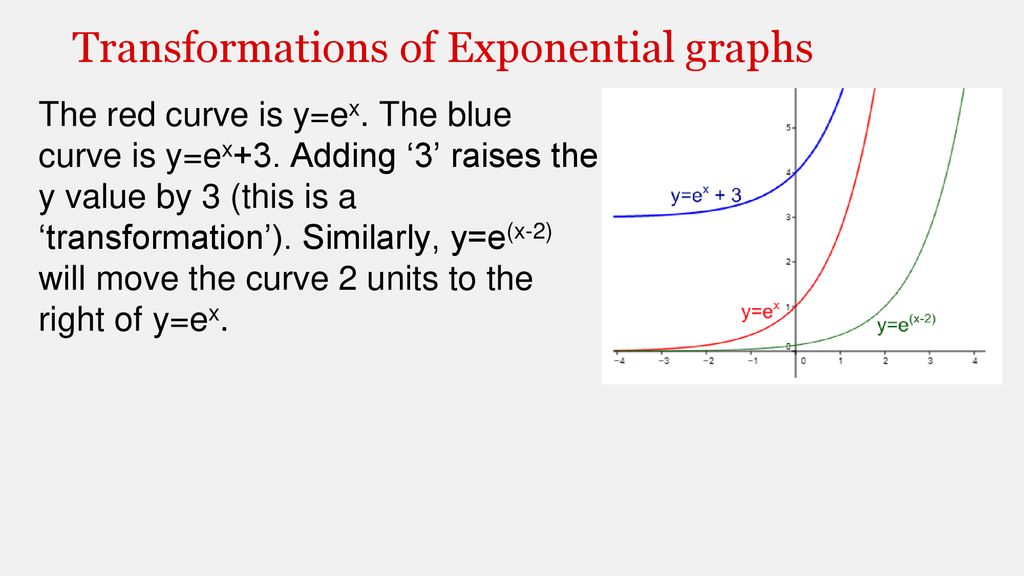
Transformations are changes to the graph Transformations include vertical shifts, horizontal shifts, and graph reversals Changing the sign of the exponent will result in aOf integration while I try to come up with the transformation to use After staring at the problem for a while, I start to notice some patterns (x y) shows up in a lot of places it's mentioned twice in the description of R, it appears in the integrand, and in fact if I write (x y)ex2 y2 = (x y)e(xy)(x y)Function Transformations Just like Transformations in Geometry, we can move and resize the graphs of functions Let us start with a function, in this case it is f(x) = x 2, but it could be anything f(x) = x 2 Here are some simple things we can do to move or scale it on the graph




Stretching And Reflecting Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation
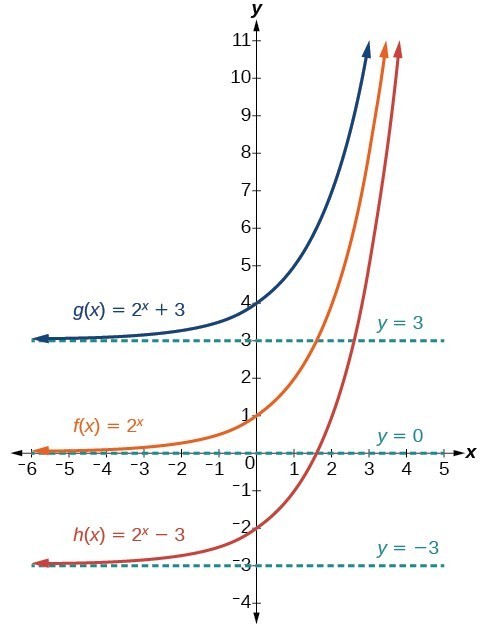



Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra
Transformations "before" the original function We could also make simple algebraic adjustments to f(x) before the function f gets a chance to do its job For example, f(xd)isthefunctionwhere you first add d to a number x, and only after that do you feed a number into the function f The chart below is similar to the chart on page 68The result of this first transformation is shown below Now, we need to apply the second transformation to the result of the first one (here, the dashed grey shape) So, we will start by drawing on the mirror line y=x (orange) Then, if you're using tracing paper, trace both the mirror line and the shape onto the tracing paper(Type your answer in interval




Stretching And Reflecting Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation



Solution Describe The Transformations On The Following Graph Of F X E X State The Placement Of The Horizontal Asymptote And Y Intercept After The Transformation For Example Horizon
Combining Transformations 10 Sketch the graph of y = (x – 3)2 4 and describe the transformations of the parent graph 11 Sketch the graph of y = 2ex 4 and describe the transformations of the parent graph 12 Sketch the graph of y = ln (x – 3) 1 and describe the transformations of the parent graphDescribe the transformations on the following graph of f(x) = e^x State the placement of the horizontal asymptote and yintercept after the transformation For example, left 1 or rotated about the yaxis are descriptions a} g(x) =e^x 2 All points of the graph move down two units Horizontal asymptote y=2Now consider a transformation of X in the form Y = 2X2 X There are five possible outcomes for Y, ie, 0, 3, 10, 21, 36 Given that the function is onetoone, we can make up a table describing the probability distribution for Y TABLE 3 ProbabilityofaFunction oftheNumberofHeadsfromTossing aCoin Four Times Y = 2 * (# heads)2 # of heads




Introduction We Are Going To Look At Exponential Functions We Will Learn About A New Special Number In Mathematics We Will See How This Number Can Be Ppt Download
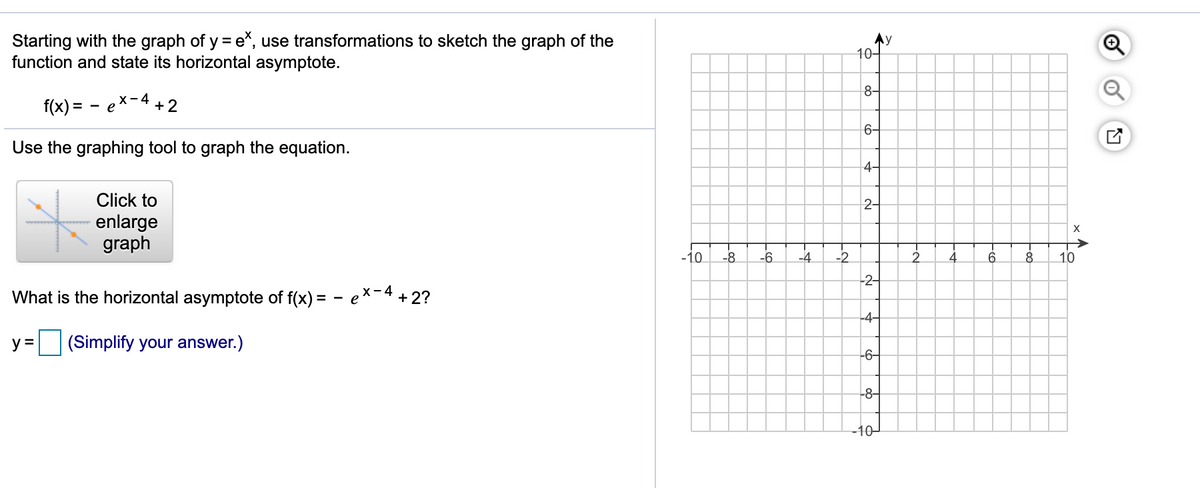



Answered Starting With The Graph Of Y E Use Bartleby
Use transformations of the graph of y=e^{x} to graph the function Write the domain and range in interval notation (See Example 3) k(x)=e^{x}1"vertical transformations" a and k affect only the y values) Note When using the mapping rule to graph functions using transformations you should be able to graph the parent function and list the "main" points Example 3 Use transformations to graph the following functions a) h(x) = −3 (x 5)2 – 4 b) g(x) = 2 cos (−x 90°) 8We can use the transformations to sketch the graph of more complicated exponential functions Example 4 Sketch the graph and determine the domain and range g (x) = e x 2 − 3 Solution Identify the basic transformations y = e x B a s i c g r a p h y = e x 2
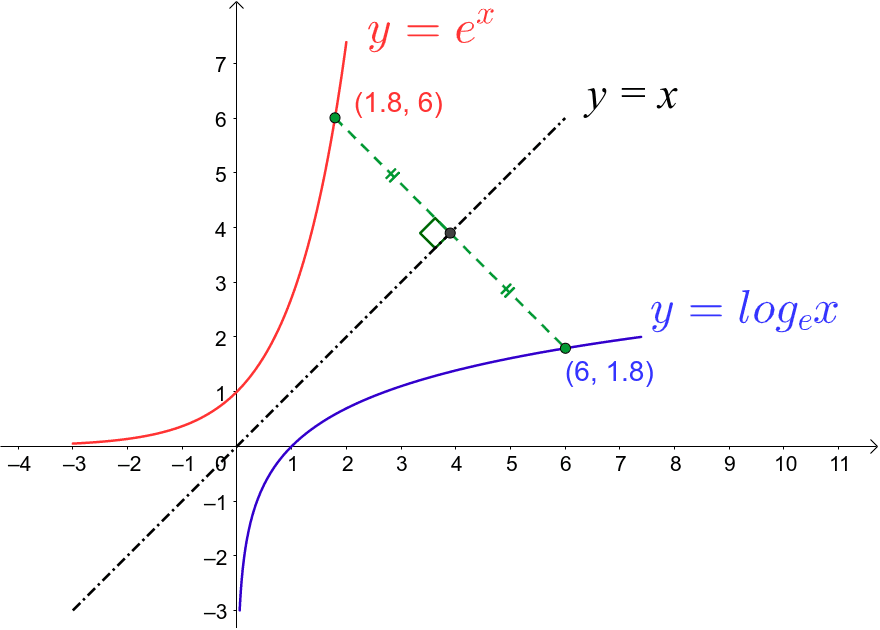



Graphs E X And Ln X Geogebra
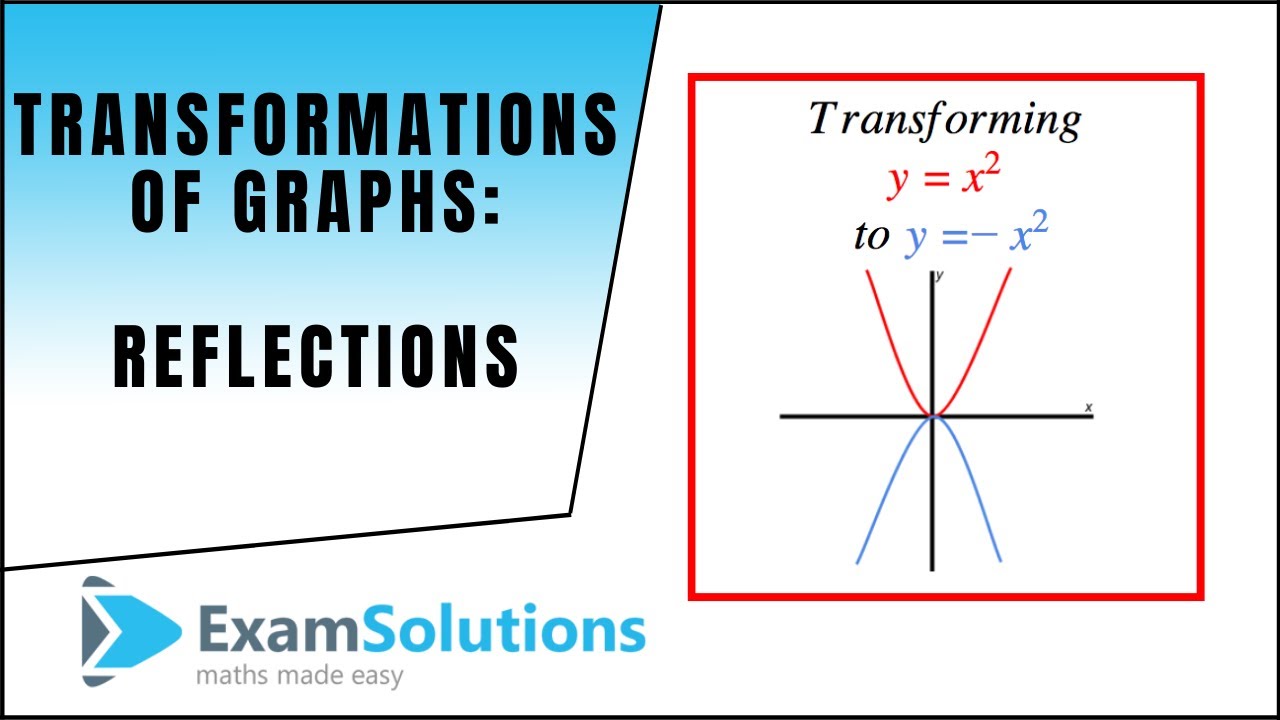



Transformations Of Graphs Reflections Y F X F X Examsolutions Youtube
Begin with the graph of y = e^x Use transformations to graph the function below Then determine its domain, range, and horizontal asymptote f(x) = 12 e^x Use the graphing tool to graph the function (For any answer boxes shown with the grapher, type an exact answer) What is the domain of f(x) = 12 e^x?Describe the transformations that were done to the parent function F(x)=X^2 to create g(x)=2(x6)^2 5 Use complete sentences Math To describe a sequence of transformations that maps triangle ABC onto triangle A''B''C'', a student starts with a reflection over the xaxis6 (8 points) Use the transformation u = x−y, v = xy to evaluate ZZ R (x−y)dA where R is the square with vertices (0,2), (1,1), (2,2) and (1,3) (The graph of R and the equation of its four edges are given in the figure below ) (0,2) (1,1) (2,2) (1,3) x y R y=x y=x2 y=4−x y=2−x Solution Notice that (u = x−y v = xy ⇒ (x = uv 2 y



Transforming Exponential Functions
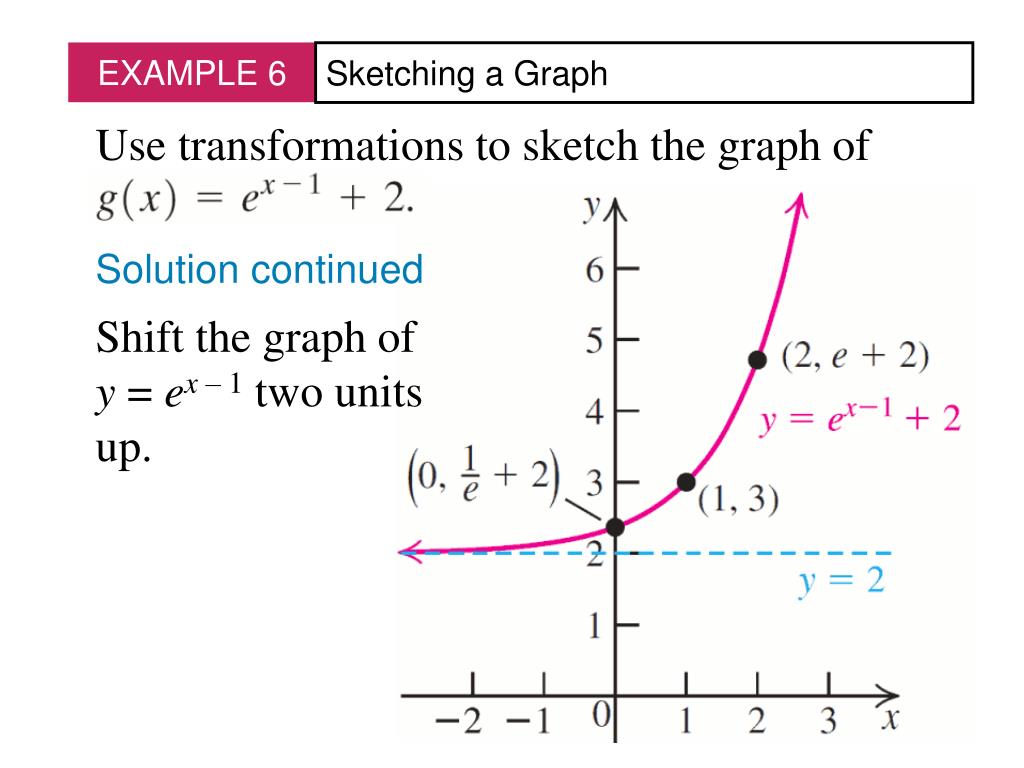



Ppt Exponential Functions Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
What is the domain of f(x) = 11e^x?Find the Laplace and inverse Laplace transforms of functions stepbystep \square!See Example 0(a)(b) from Transformation of Several Random Variablespdf X;Y are continuous { The CDF approach (the basic, o theshelf method)



What Is The Graph Of E X Quora



Transforming Exponential Functions
Begin with the graph of y=e^{x} (Figure 27) and use transformations to graph each function Determine the domain, range, horizontal asymptote, and y intercept Boost your resume with certification as an expert in up to 15 unique STEM subjects this summerMore generally, an exponential function is a function of the form f ( x ) = a b x , {\displaystyle f (x)=ab^ {x},} where b is a positive real number, and the argument x occurs as an exponent For real numbers c and d, a function of the form f ( x ) = a b c x d {\displaystyle f (x)=ab^ {cxd}} is also an exponential function, since it can beExample Use transformations to graph f(x) = 3x 2 Start with a basic function and use one transformation at a time Show all intermediate graphs This function is obtained from the graph of y = 3x by first reflecting it about yaxis (obtaining y = 3
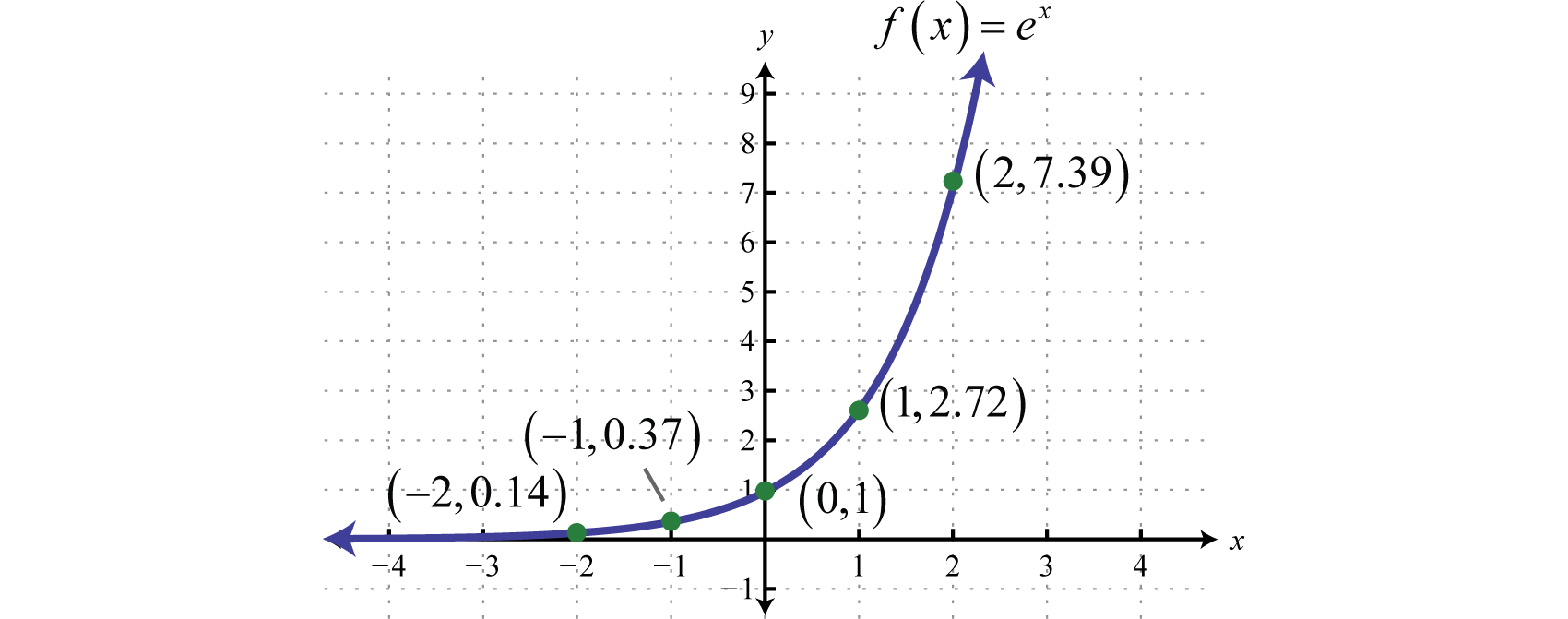



Exponential Functions And Their Graphs



Www Pmschools Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 701 Dataid 3614 Filename 15 composition of transformations answers Pdf
Y = abx−h k y = a b x h k Find a a, h h, and k k for g(x) = (e)x g ( x) = ( e) x a = 1 a = 1 h = 0 h = 0 k = 0 k = 0 The horizontal shift depends on the value of h h The horizontal shift is described as f (x) = f (xh) f ( x) = f ( x h) The graph is shifted to the left h h units👉 Learn how to graph exponential functions in base e An exponential function is a function whose value increases rapidly e is a constant called the expone4 TRANSFORMATIONS OF RANDOM VARIABLES FY (y)=P(Y ≤ y) = P eX ≤ y = P(X ≤ lny),y>0 = Z ln y −∞ 1 √ 2πσ2 exp − (x− µ)2 2σ2 dx, y>0 (11) NowdifferentiateFY (y)toobtainthedensityfunctionf(y) In thiscasewewillneedtherulesfor differentiating under the integral sign They are given by theorem2 which we statebelowwithout proof Theorem 2
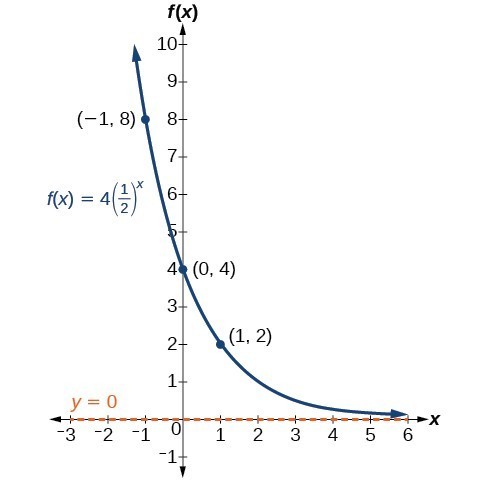



Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra



Exponential Curve Transformations Graphing Advice The Student Room
Graphing a function is not as simple as creating a table and plotting those points Functions can get very complex and go through transformations, such as flips, shifts, stretching and shrinking, making the usual graphing techniques difficult This article will provide the necessary information to correctly graph these transformations of functions571 Determine the image of a region under a given transformation of variables 572 Compute the Jacobian of a given transformation 573 Evaluate a double integral using a change of variables 574 Evaluate a triple integral using a change of variables Change of Variables for Double Integrals We have already seen that, under the change of variables T(u, v) = (x, y) where x = g(u, v) and y = h(u, v), a small region ΔA in the xy plane is related to the area formed by the product ΔuΔv in the uv




Use The Graph Of Y E And Transformations To Sketch Chegg Com




Function Transformations
It is a reflection across the yaxis of f(x)=e^x I'm going to assume you mean the transformation from the parent function f(x) = e^x Let's think about how to get e^x from f(x) You would have to plug in x instead of x, giving f(x)=e^x Therefore we can say that h(x) = f(x) What does this mean as far as transformation on a graph?Y E X Transformations Solution Describe The Transformations On The Following Graph Of F X E X State The Placement Of The Horizontal Asymptote And Y Intercept After The Transformation For Example Horizon For more information and source, see on this link httpsIdentify function transformations Our mission is to provide a free, worldclass education to anyone, anywhere Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization
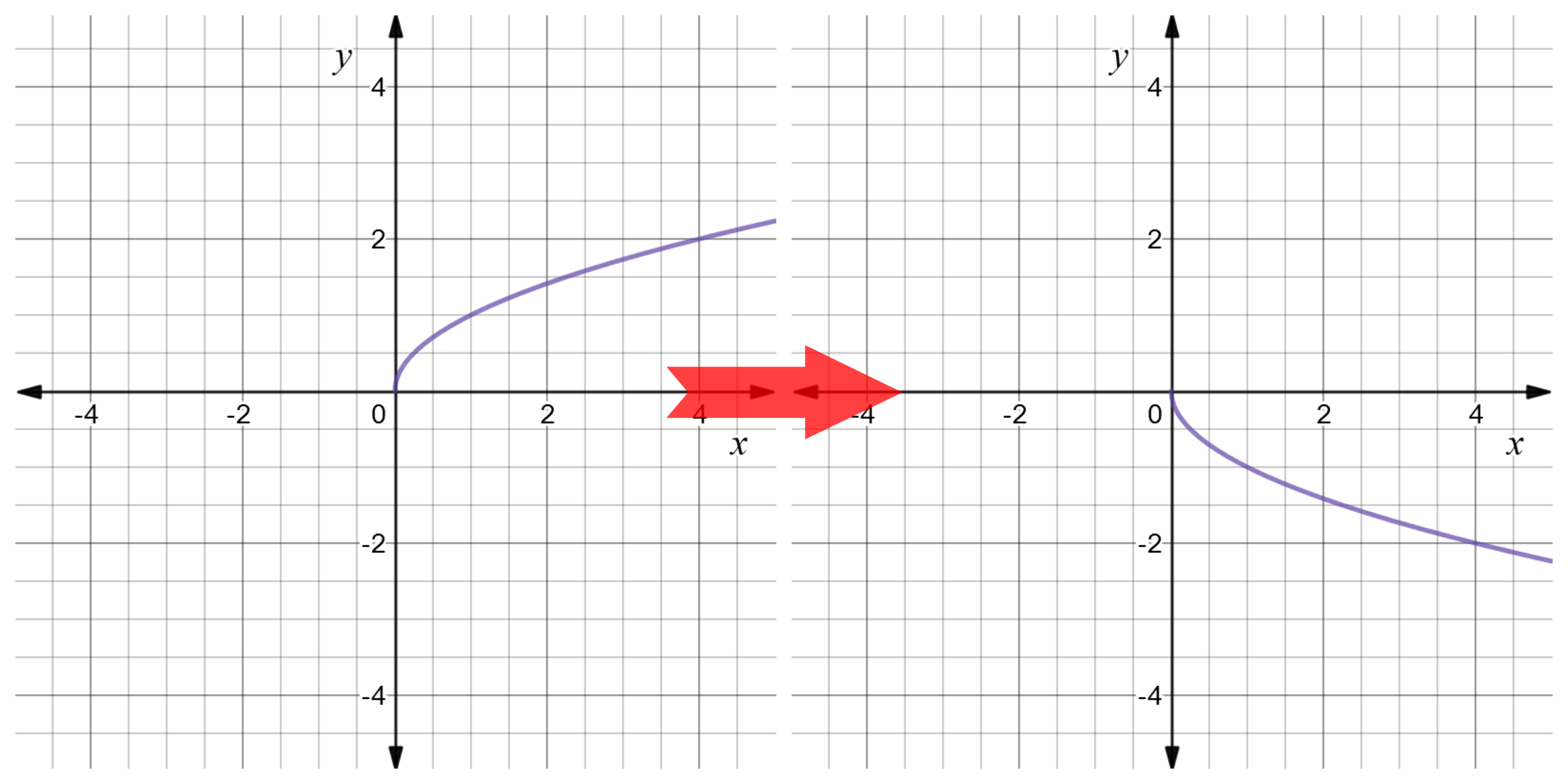



Reflect Function About Y Axis F X Expii



Transformation Of Y X 2 And Y X 3 Geogebra
Begin with the graph of y = e^x Use transformations to graph the function below Then determine its domain, range, and horizontal asymptote f(x) = 11 e^x Use the graphing tool to graph the function (For any answer boxes shown with the grapher, type an exact answer) What is the domain of f(x) = 11 e^x?Well The point (2, e^2) on f(x) willCalculate the Jacobian of the transformation (x,y) → (u,v) and write down the differential through the new variables dxdy = ∣∣ ∣ ∂(x,y) ∂(u,v) ∣∣



Parent Functions Types Properties Examples




6 Of 13 Begin With The Graph Of Y Ex Use Transfo Gauthmath
The easiest case for transformations of continuous random variables is the case of gonetoone We rst consider the case of gincreasing on the range of the random variable X In this case, g 1 is also an increasing function To compute the cumulative distribution of Y = g(X) in terms of the cumulative distribution of X, note that F but which transformation comes first , and what's the difference if I switched them (in both cases)?E(aX) =aE(X) in the second equality and E(X Y) = E(X)E(Y) in the third equality are utilized, where X and Y are random variables and a is a constant value 139 The variance of X is computed as follows V(X) =V(1 n n i=1 X Transformation of variables is used in the case of continuous random variables Based on a distribution of a random



Graphing Transformations Of Parent Functions Youtube
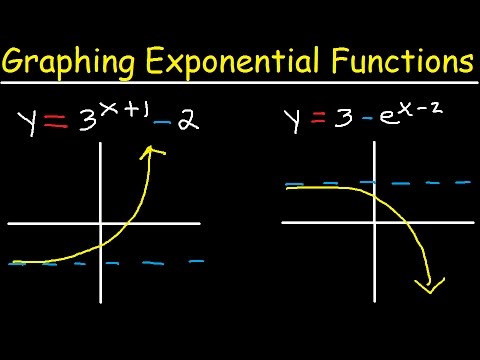



Graphing Exponential Functions With E Transformations Domain And Range Asymptotes Precalculus Youtube
Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutesThank you in advance There is no single "correct" sequence of transformations to get either of theseTransformations U = X Y, and V = X − Y (a) (3 points) Derive E(U) and E(V) in terms of µX and µY E(U) = E(XY) = E(X) E(Y) = µX µY E(V) = E(X − Y) = E(X) − E(Y) = µX − µY (b) (5 points) Derive E(U V) in terms of µX, µY, and 2 σX 2 σY Hint you want the expected value of U times V Use the definitions at the top of
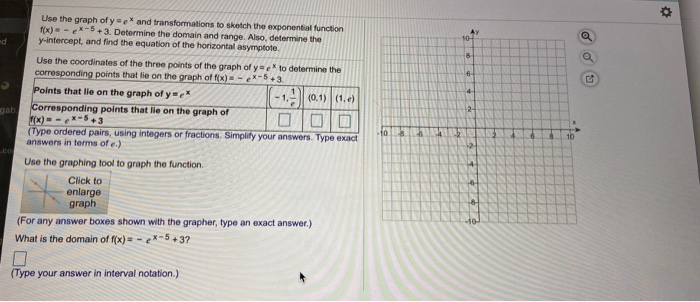



Use The Graph Of Y E And Transformations To Sketch Chegg Com



Solution Describe The Transformations On The Following Graph Of F X E X State The Placement Of The Horizontal Asymptote And Y Intercept After The Transformation For Example Left




Videos




Transformations Exponential And Logarithm Functions Kus Objectives Bat



Biomath Transformation Of Graphs




Transforation Of Exponential Graphs Y Ex Matching Cards With Answers Teaching Resources
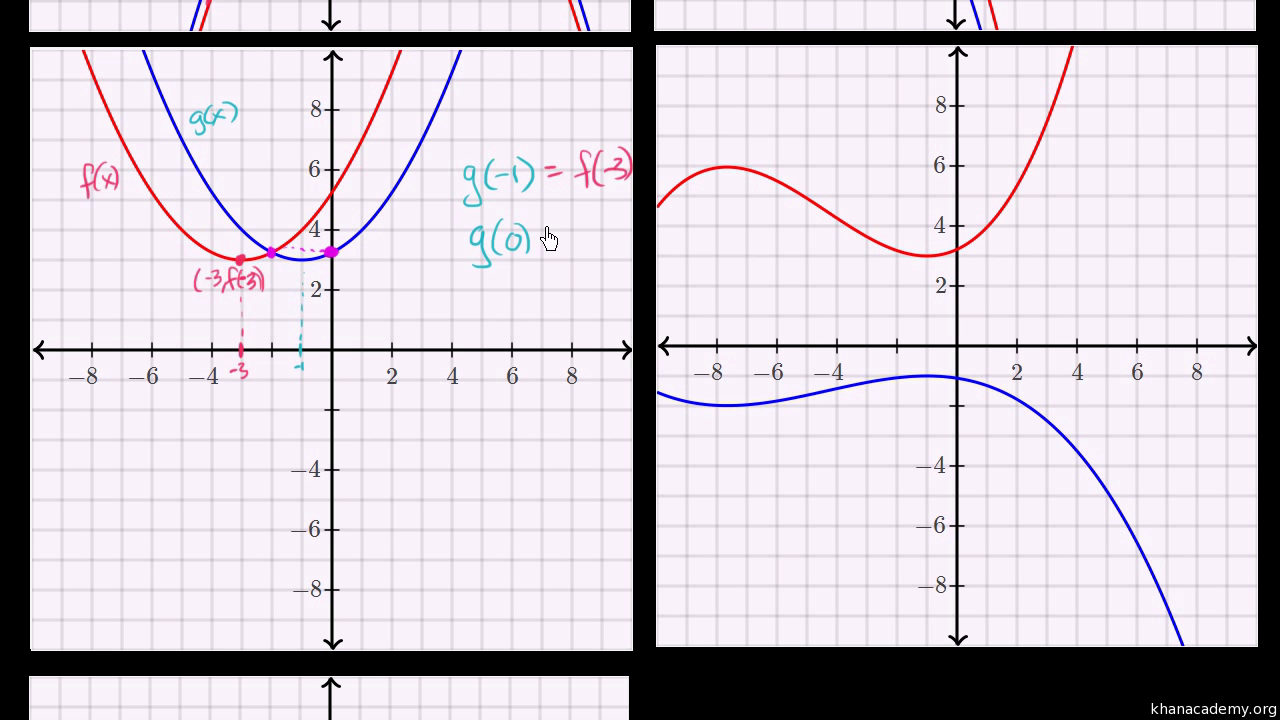



Identifying Function Transformations Video Khan Academy
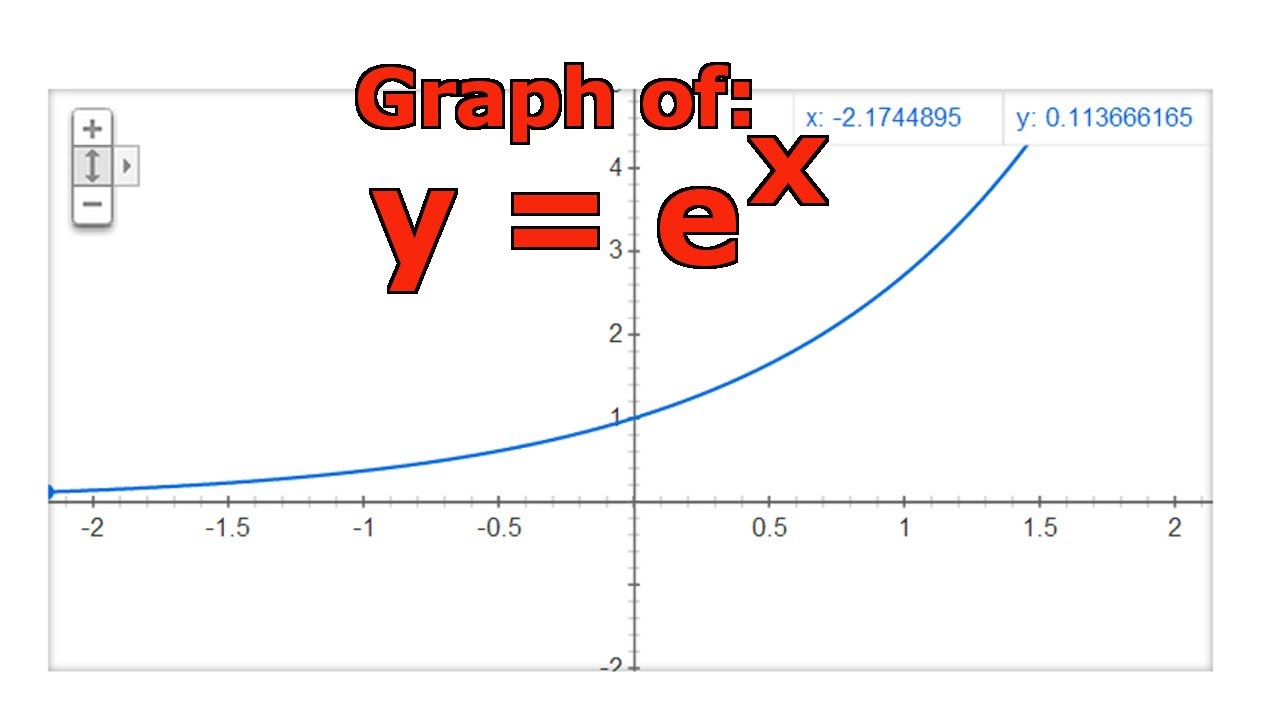



Graphing The Natural Exponential Function Y E X Youtube




Given Image A B C D E If The Pre Image Contained Point A 1 5 Which Of The Transformations Brainly Com




Transformation Of Graphs By Modulus Function Functions Openstax Cnx




Unit 1 Function Transformations 1 3 Combining Transformations



How To Reflect A Graph Through The X Axis Studypug




C3 Transformations
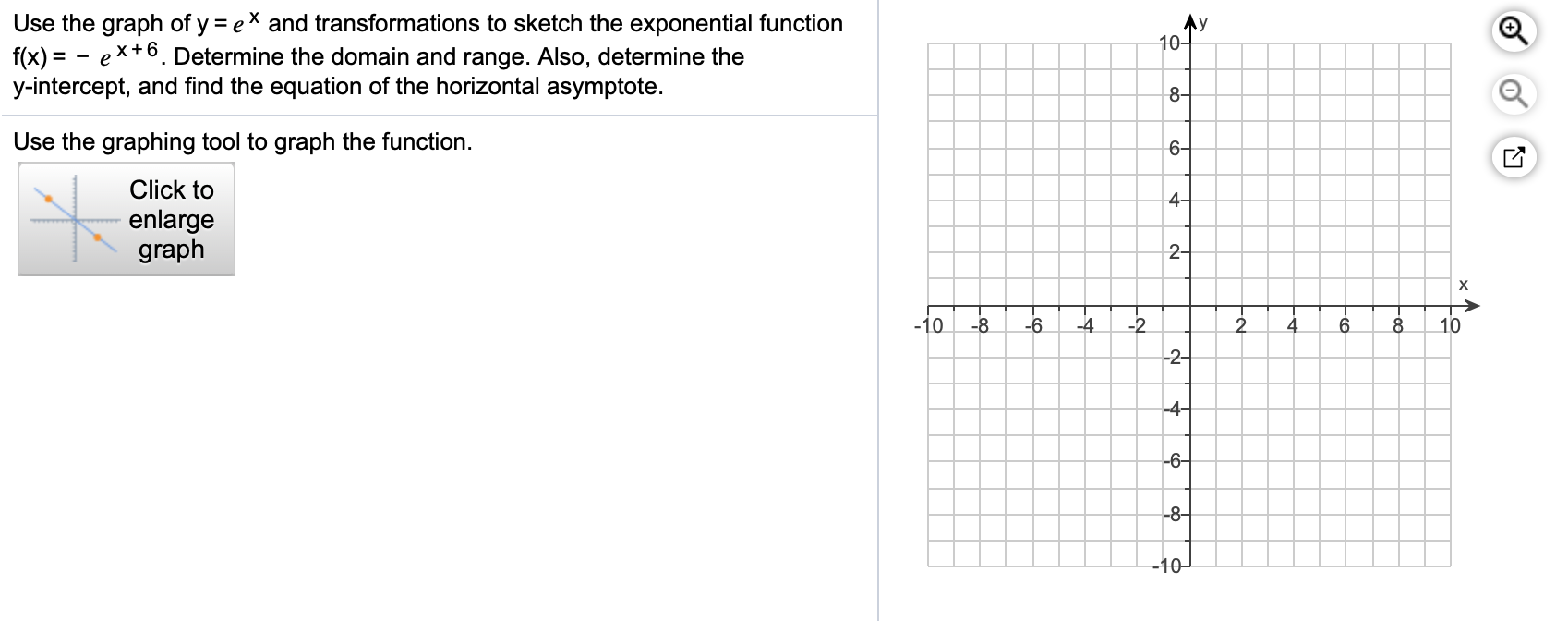



Use The Graph Of Y Ex And Transformations To Sketch Chegg Com



Reflect Function About Y Axis F X Expii




Begin With The Graph Of Y E X And Use Transformations To Graph The Following Function Determine The Domain Range And Horizontal Asymptote Of The Function F X 8e X Study Com



Logarithms And Exponentials Ppt Download



1




Function Transformations
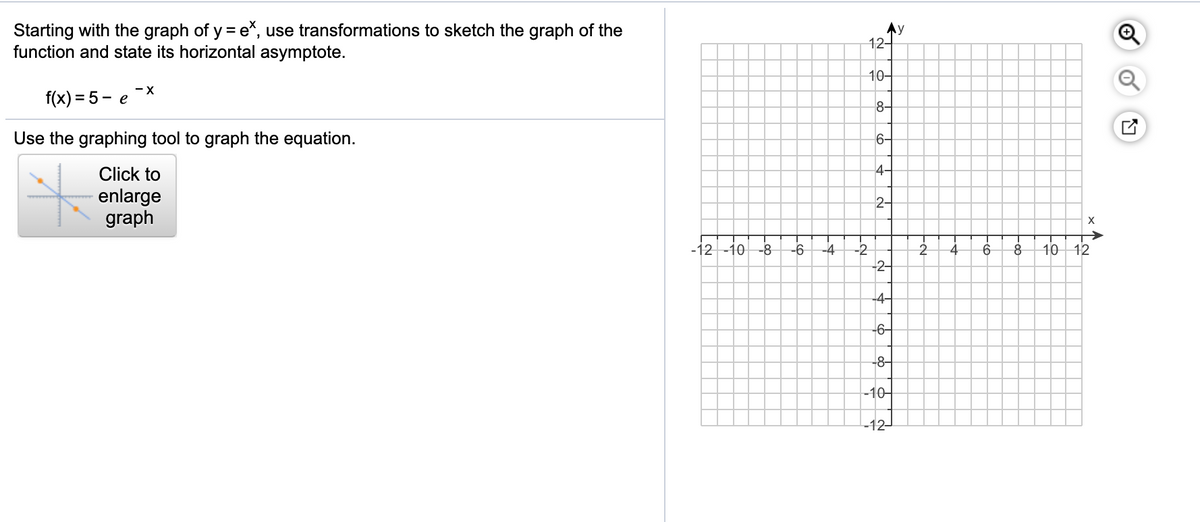



Answered Starting With The Graph Of Y E Use Bartleby



Bestmaths
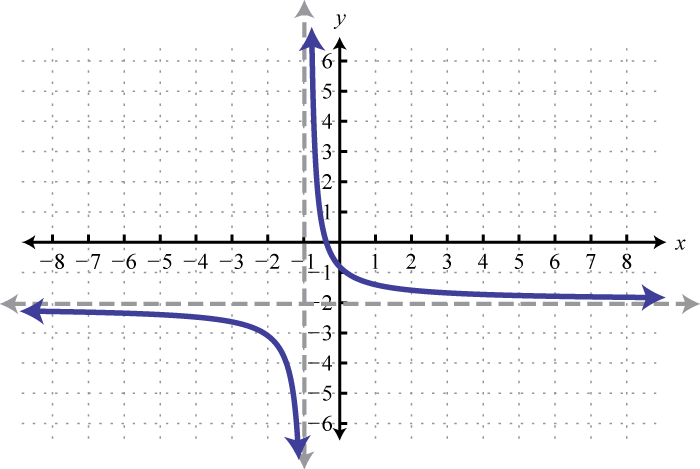



Using Transformations To Graph Functions
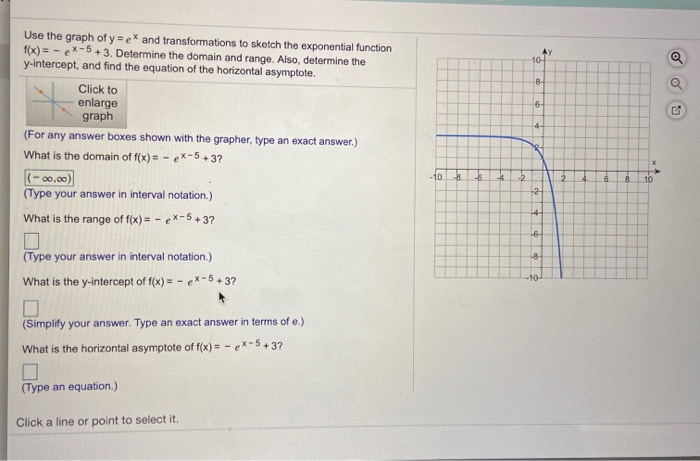



Use The Graph Of Y Ex And Transformations To Sketch Chegg Com



1
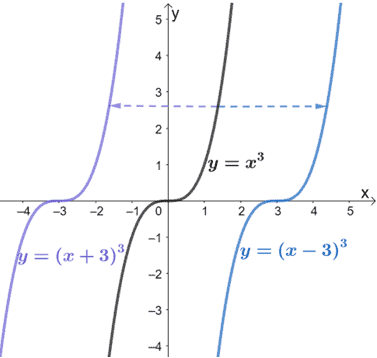



Transformations Of Functions Explanation Examples



Exponential Functions And Their Graphs



Q Tbn And9gcs Ihr455cjf 0er79a5phnv61wgyglqfjxx7pi 4elnzyjou Usqp Cau




Which Transformations To The Graph Of Y Ex Would Result In The Graph Of Y Ex 34 Brainly Com
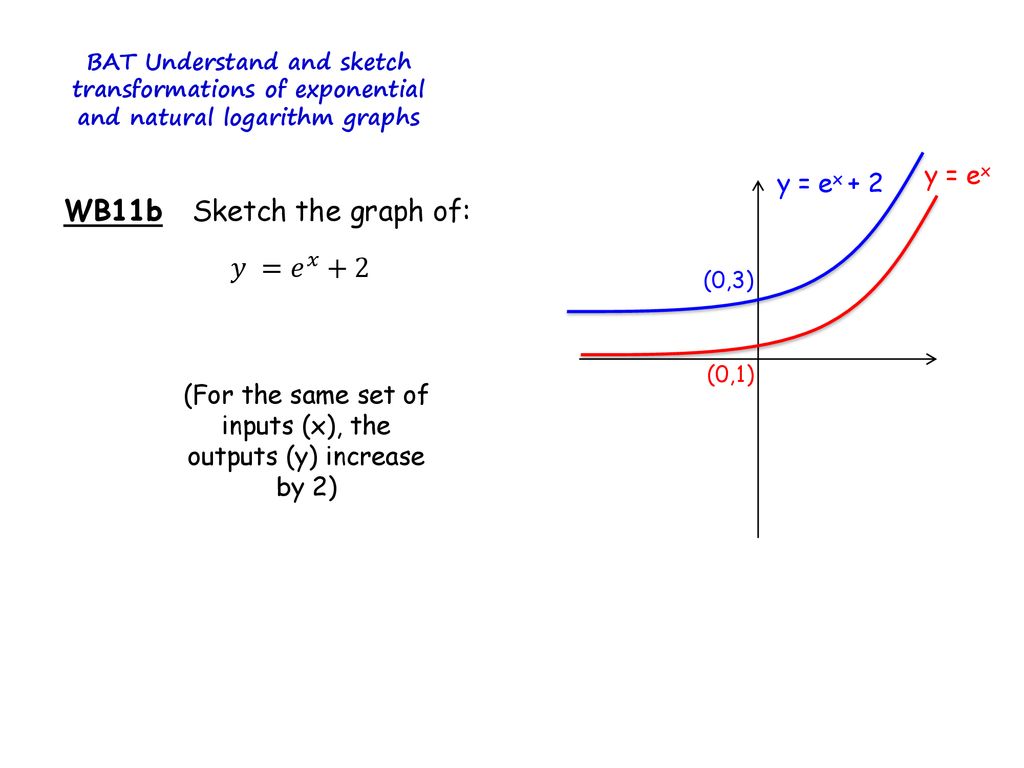



Exponential And Logarithms Transformations Graphs Ppt Download




Use The Graph Of Y E And Transformations To Sketch The Exponential Function F X New Determine Homeworklib




Begin With The Graph Of Y E X And Use Transformations To Graph The Following Function Determine The Domain Range And Horizontal Asymptote Of The Function F X 8e X Study Com




Exponential Functions Define An Exponential Function Graph Exponential Functions Use Transformations On Exponential Functions Define Simple Interest Ppt Download



Transforming Exponential Functions



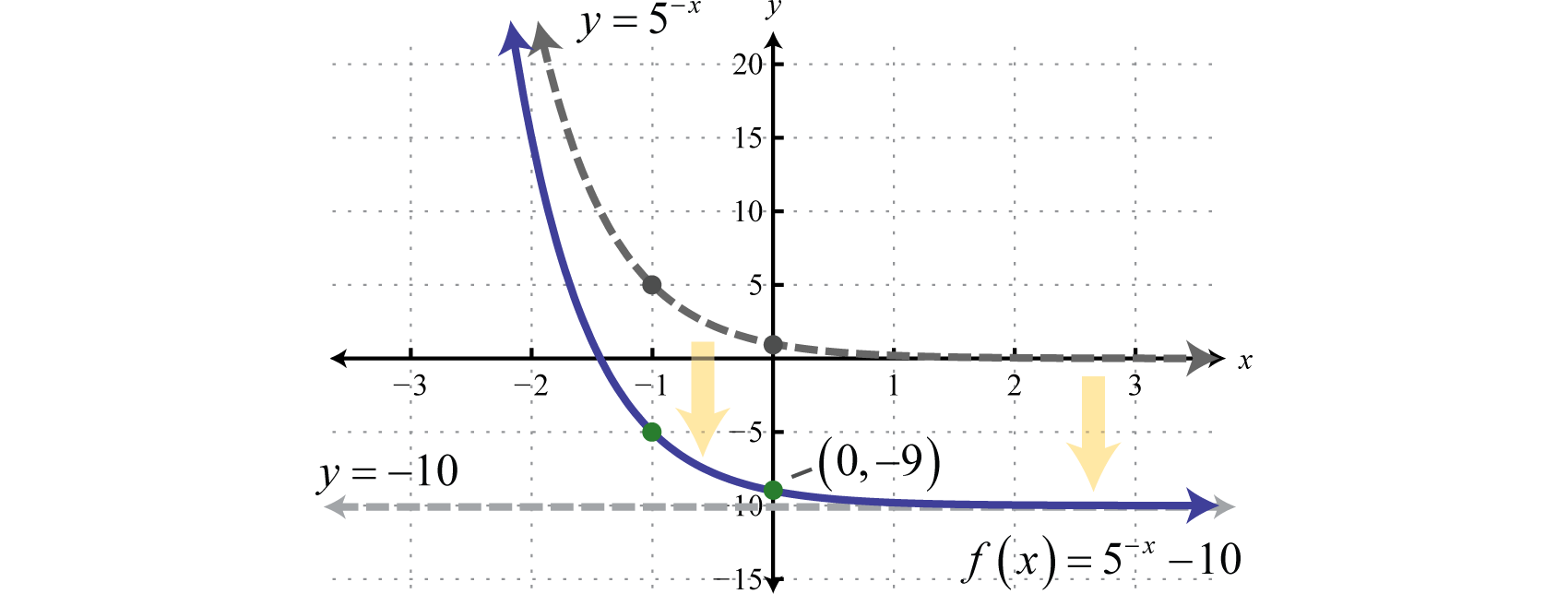
4 1 4 3 Notes



Transforming Exponential Functions
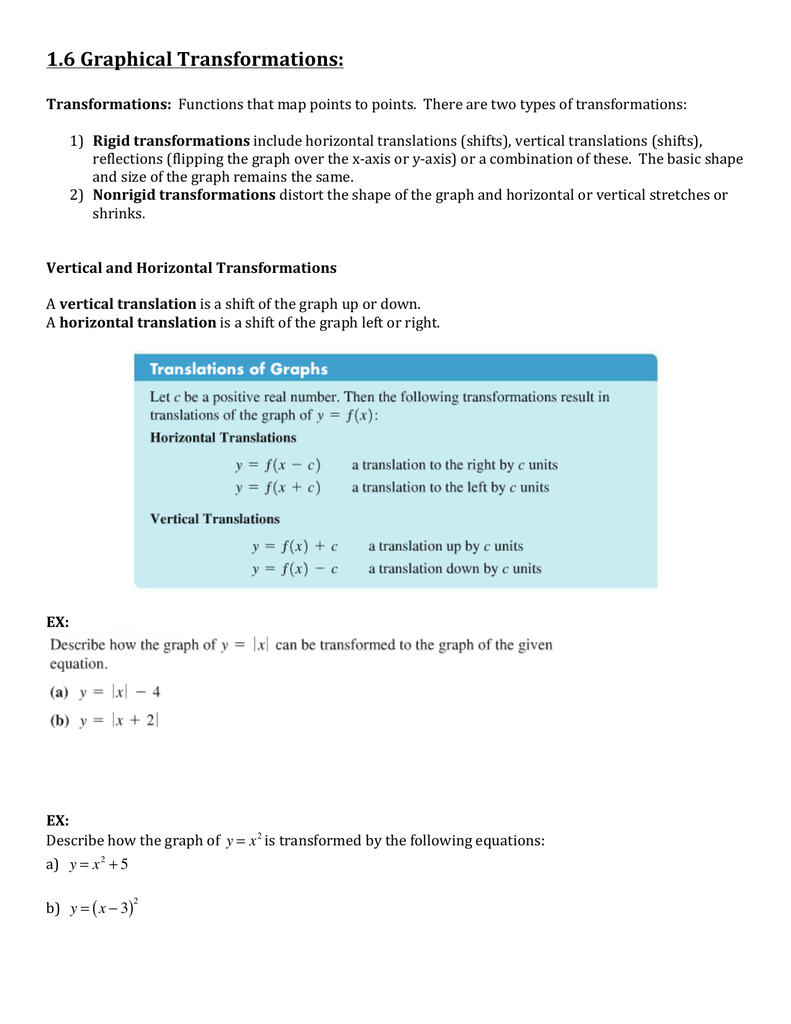



Document




Natural Exponential Graphs Iitutor
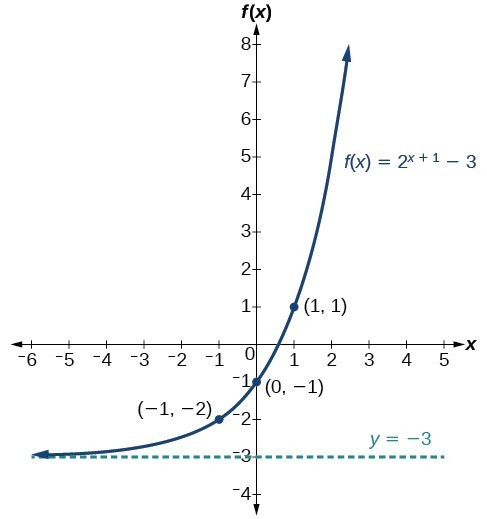



Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra
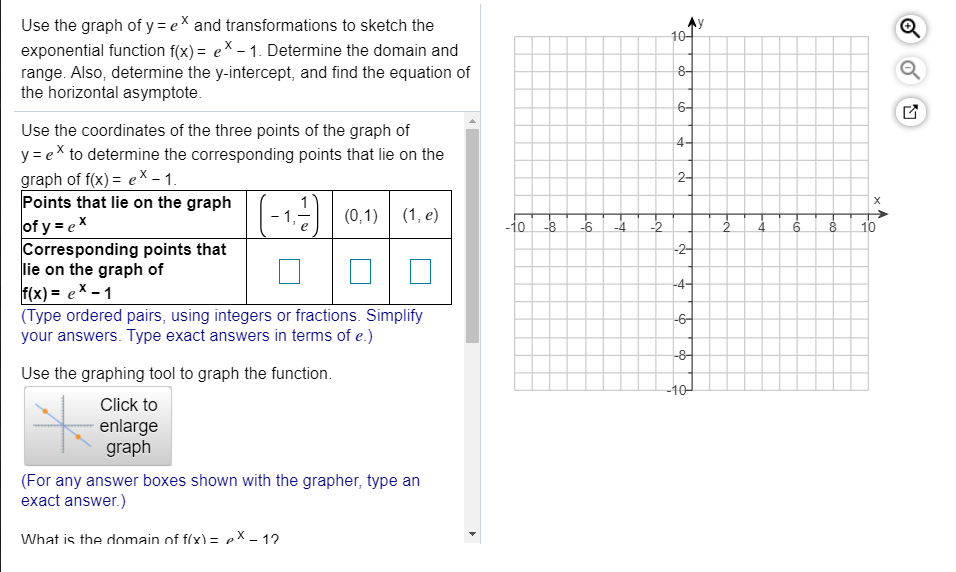



Use The Graph Of Y Ex And Transformations To Sketch Chegg Com
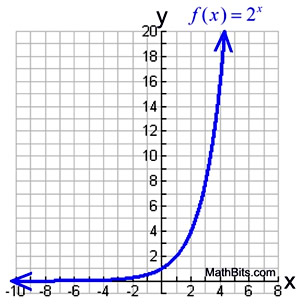



Exponential Functions Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math




Could You Explain Why Frac D Dx E X E X Intuitively Mathematics Stack Exchange
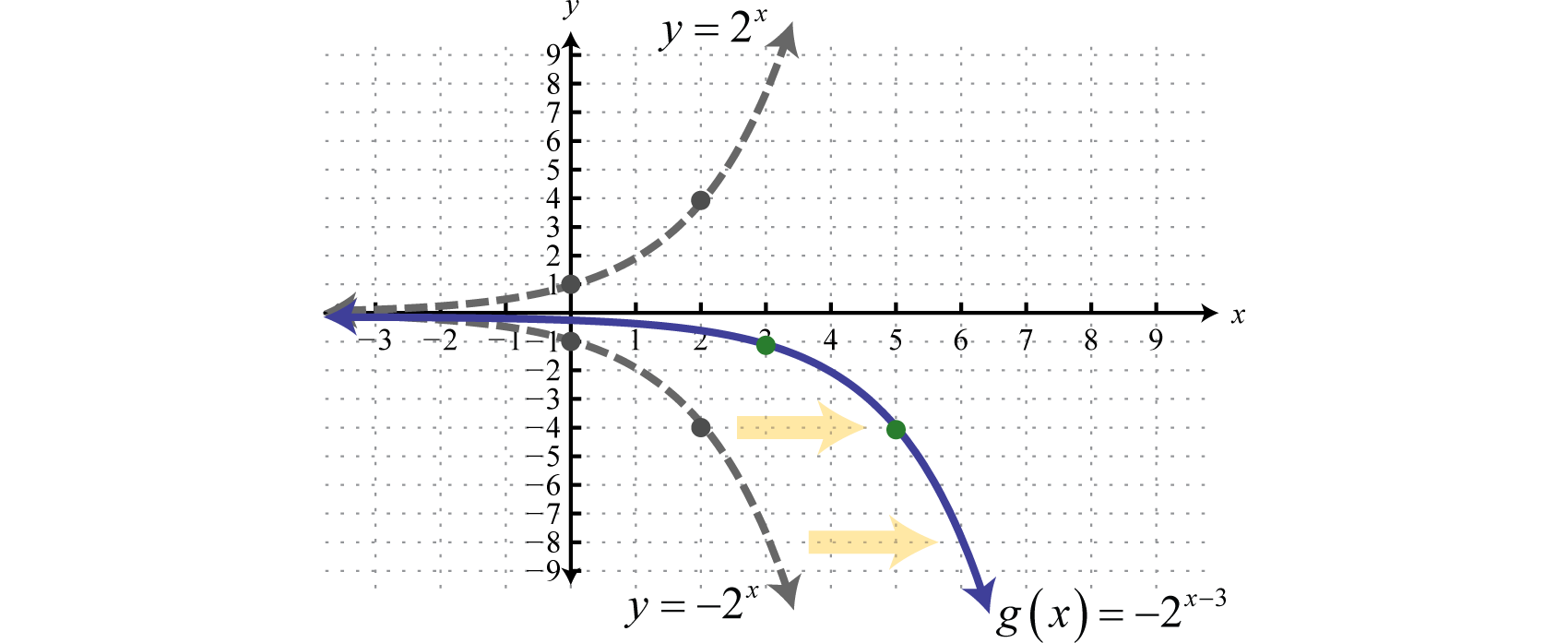



Exponential Functions And Their Graphs



Bestmaths



Solved Use The Graph Of Y E And Transformations To Sketc Chegg Com
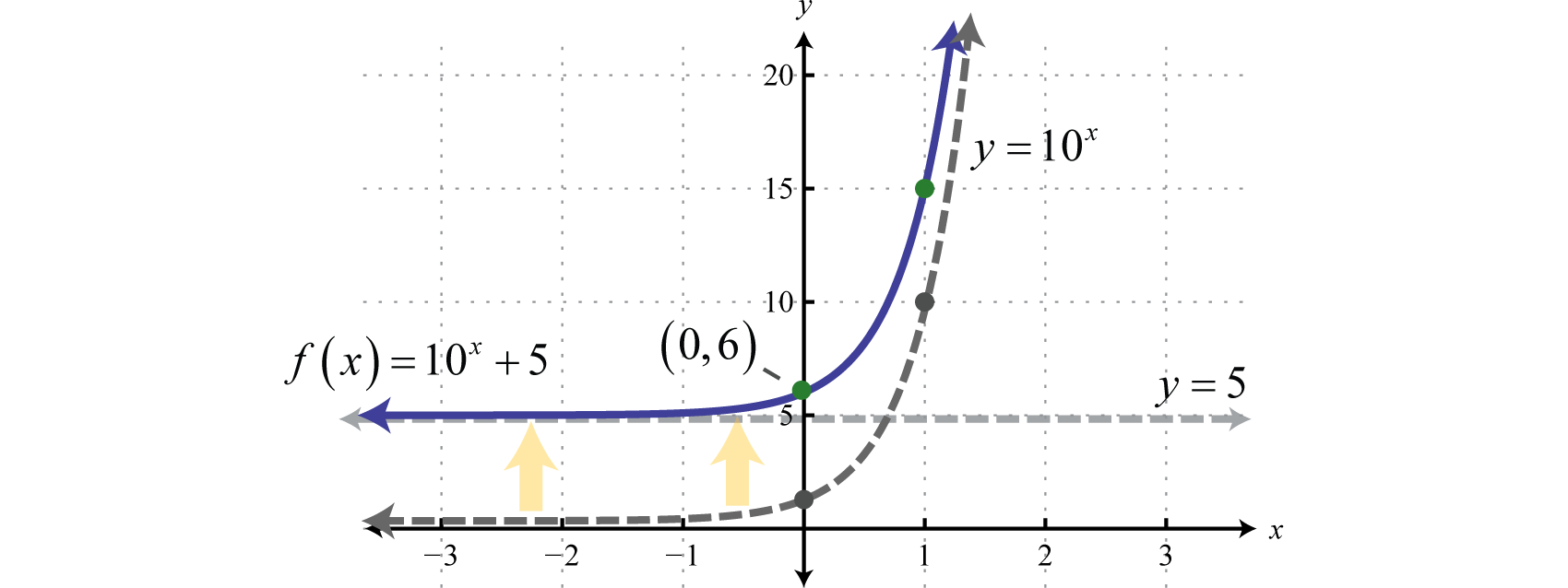



Exponential Functions And Their Graphs
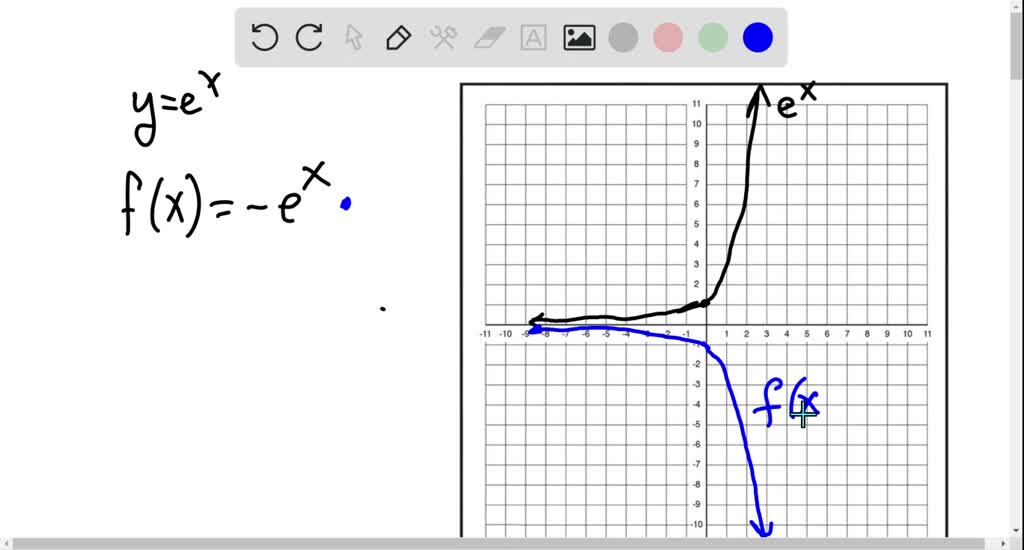



Solved 7 14 Graph The Function Not By Plotting




Describe An Exponential Function Transformation Y E X 3 Youtube
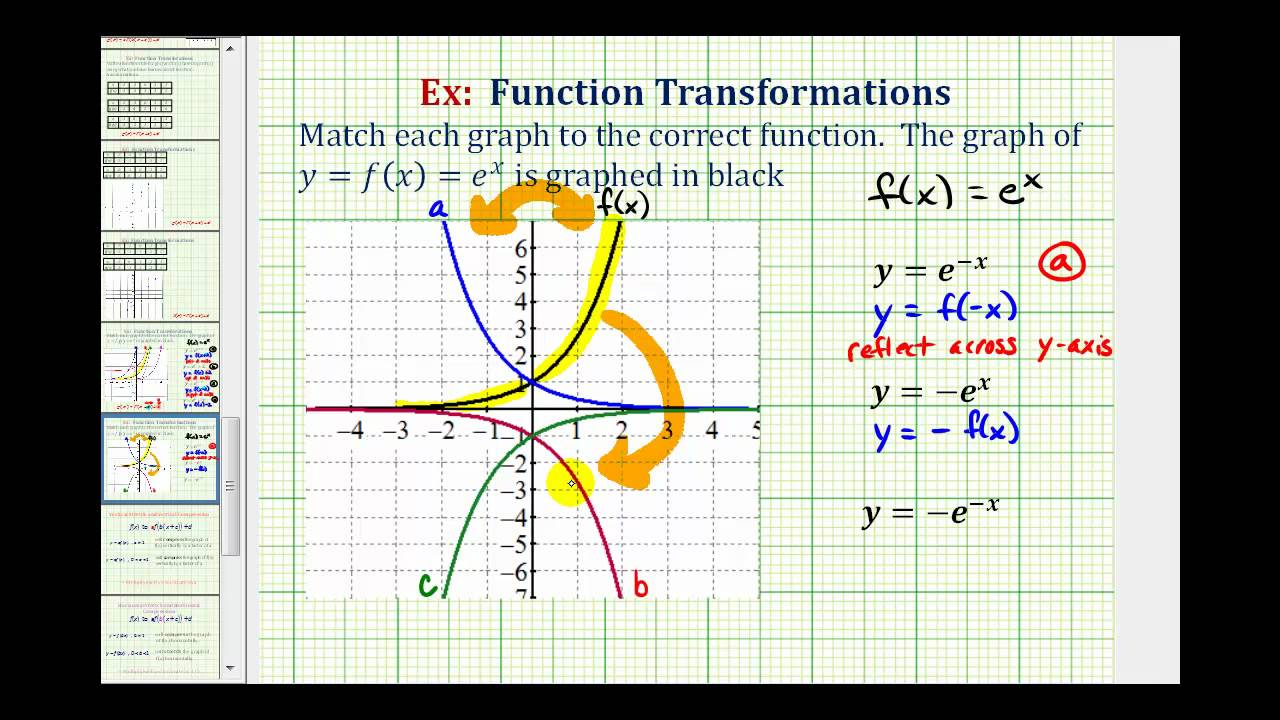



Ex Match The Graphs Of Reflected Exponential Functions To Equations Youtube



Bestmaths



3



Transformation In Y E X Physics Forums




Exp And Log Transformations Logarithmic Functions Parent Functions Scientific Notation
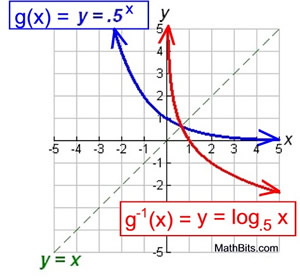



Exponential Functions Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math
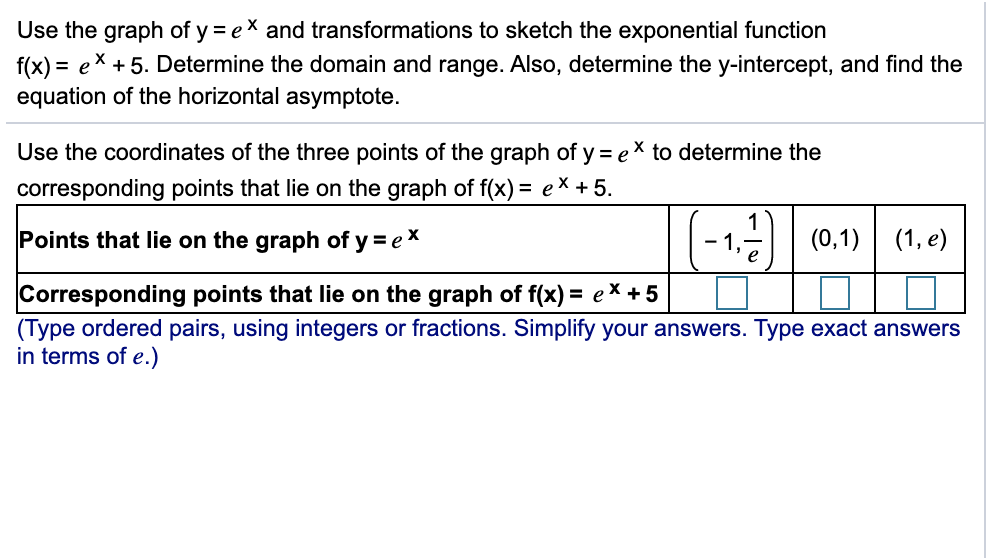



Use The Graph Of Y Ex And Transformations To Sketch Chegg Com
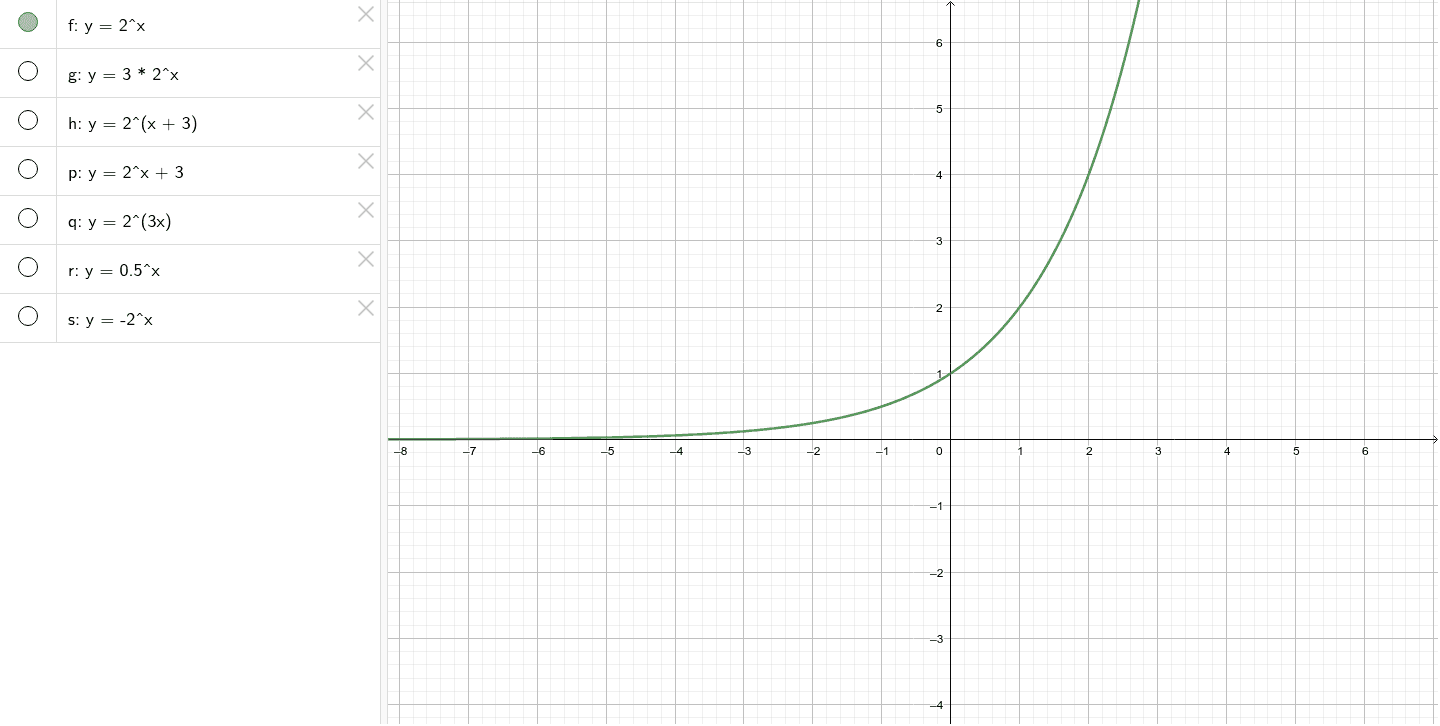



Transformations Of Y 2 X Geogebra
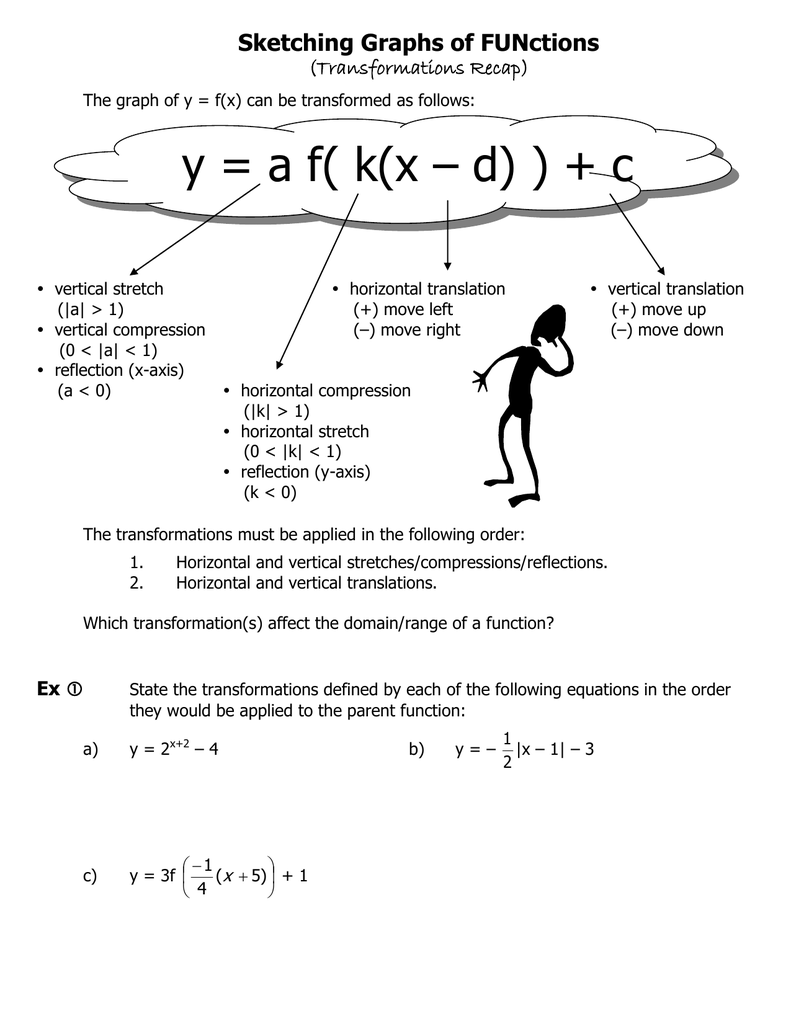



Y A F K X D C
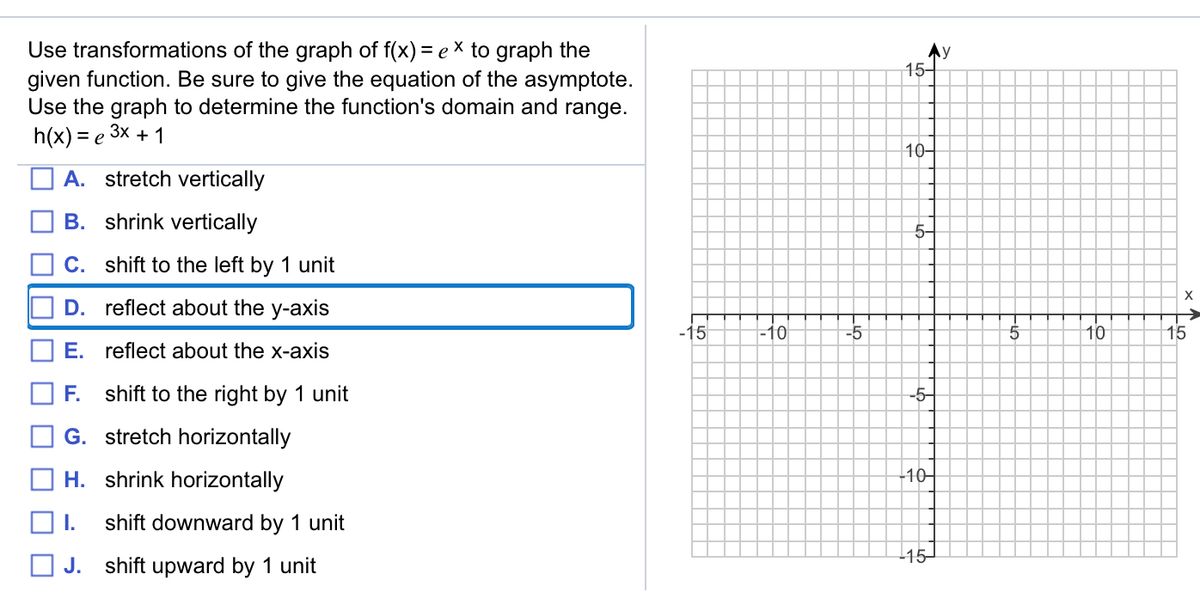



Answered Use Transformations Of The Graph Of Bartleby
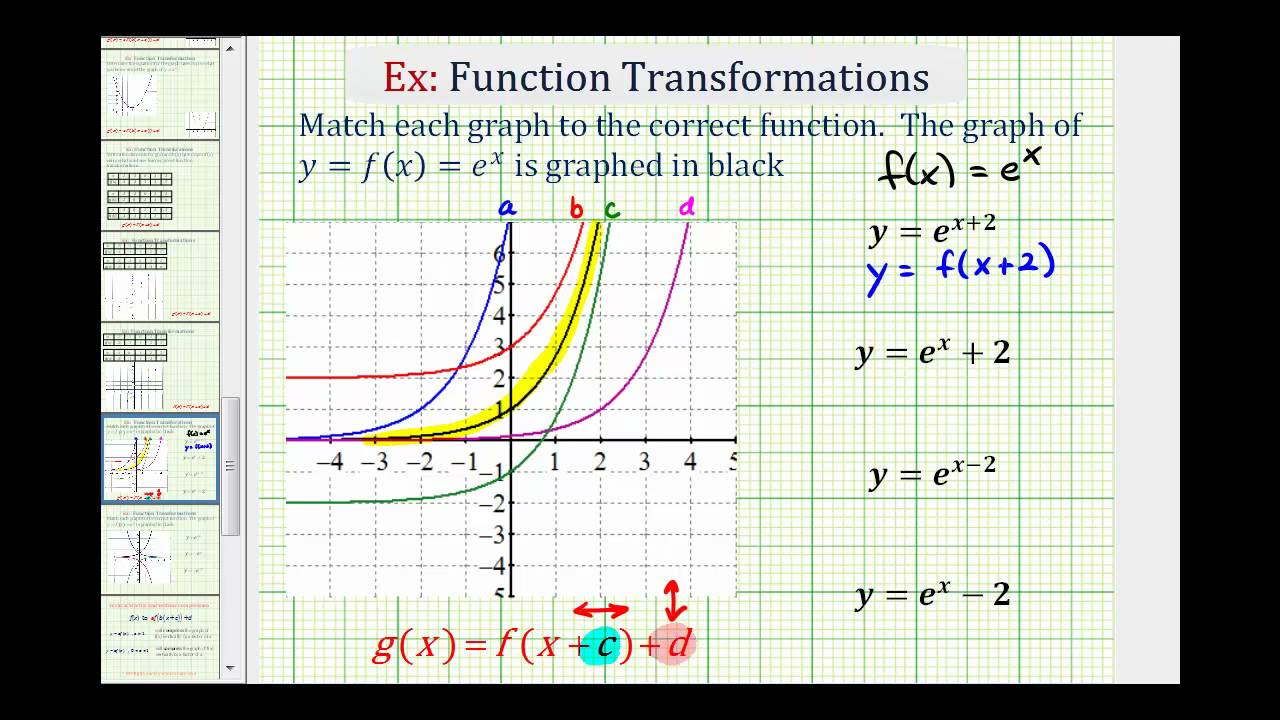



Horizontal And Vertical Translations Of Exponential Functions College Algebra




Content Linear Transformations And Matrices




Module 09 Natural Exponential Y E X



Transforming Exponential Functions



Transformations Mrs F X



Biomath Transformation Of Graphs
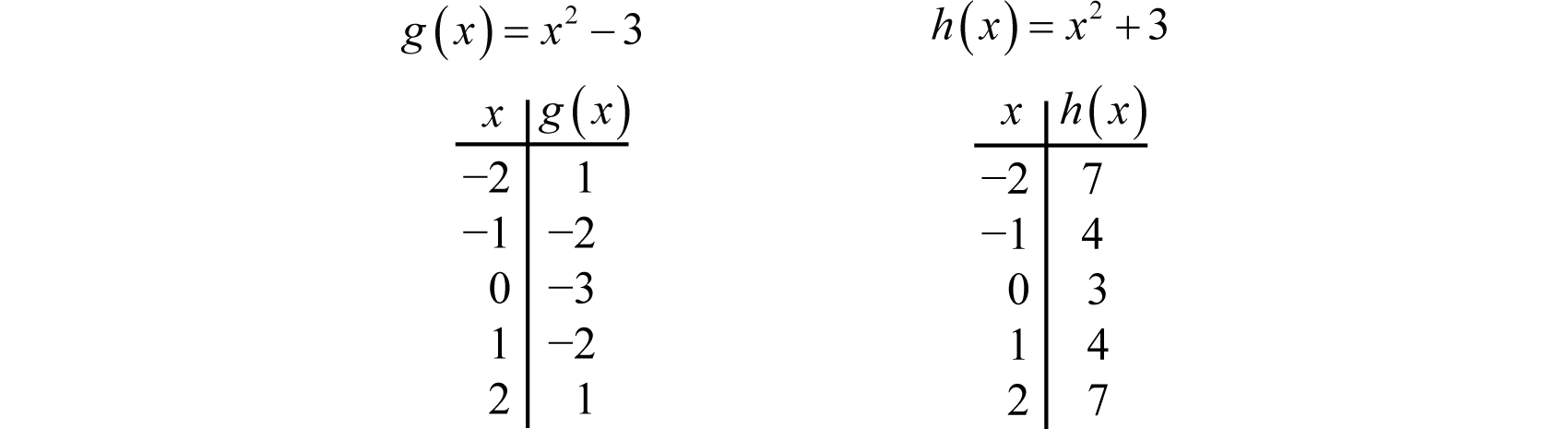



Using Transformations To Graph Functions
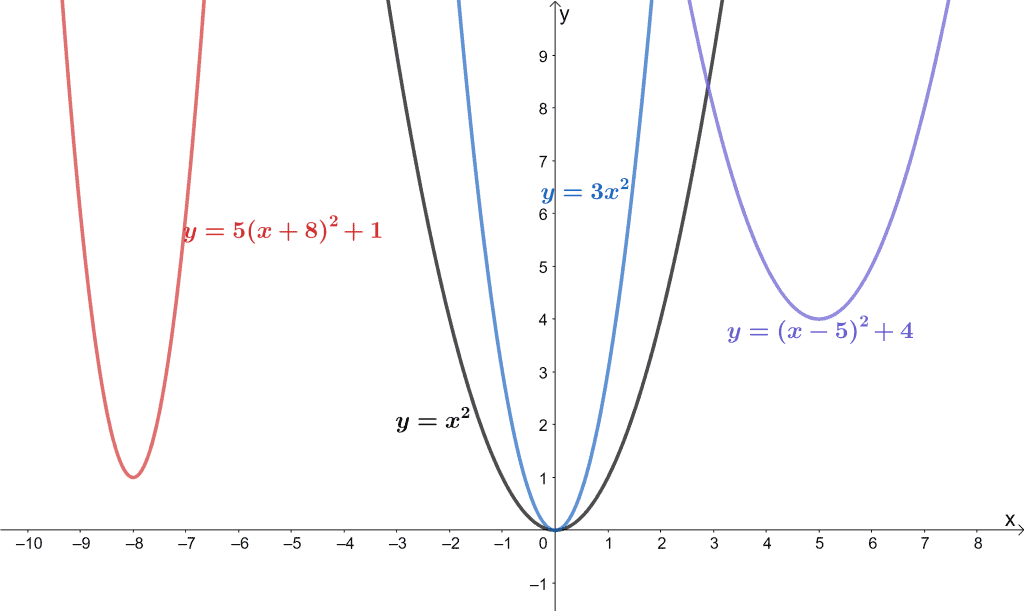



Parent Functions Types Properties Examples
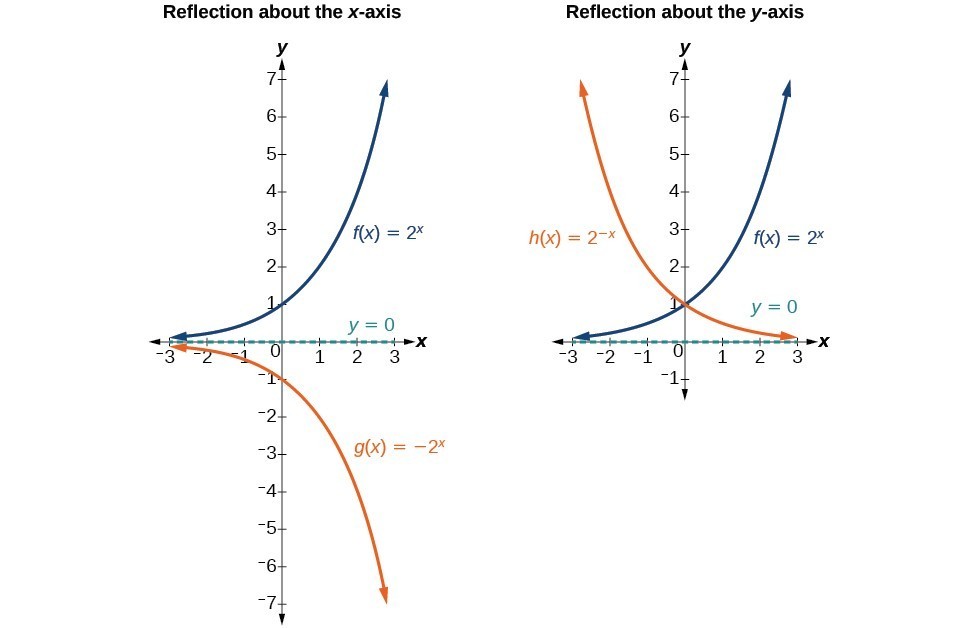



Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra



Exponetials And Growth Functions




Function Transformations
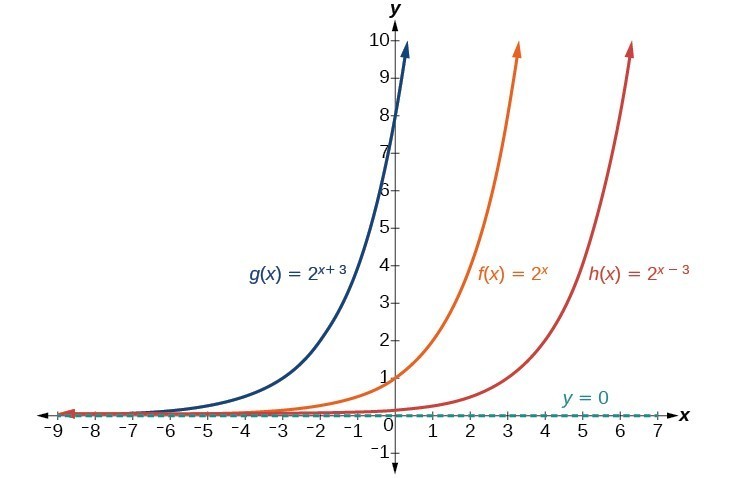



Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra
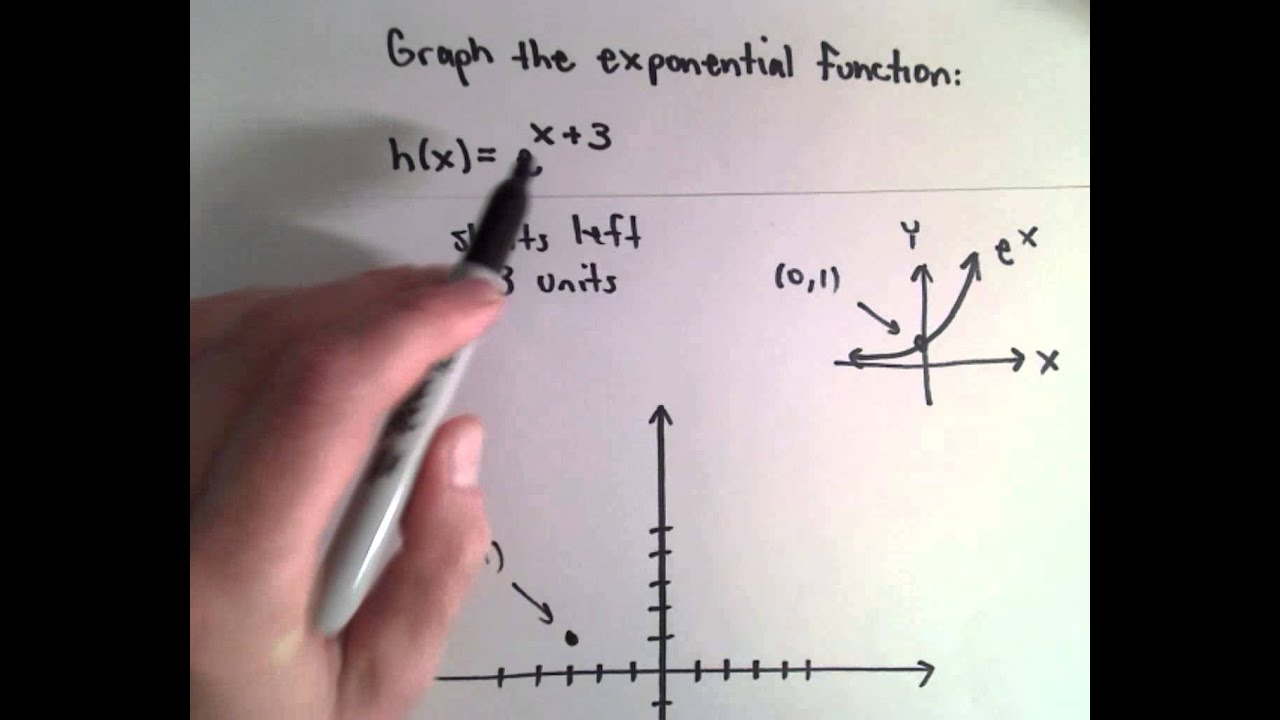



Graph Of Y E X 3 Using Graph Transformations Youtube
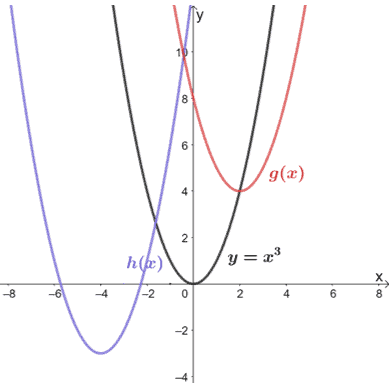



Transformations Of Functions Explanation Examples
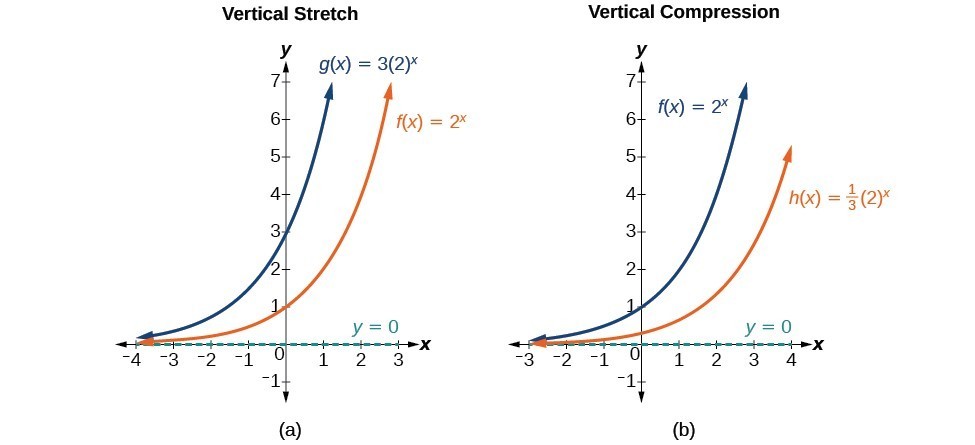



Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra



Transforming Exponential Functions
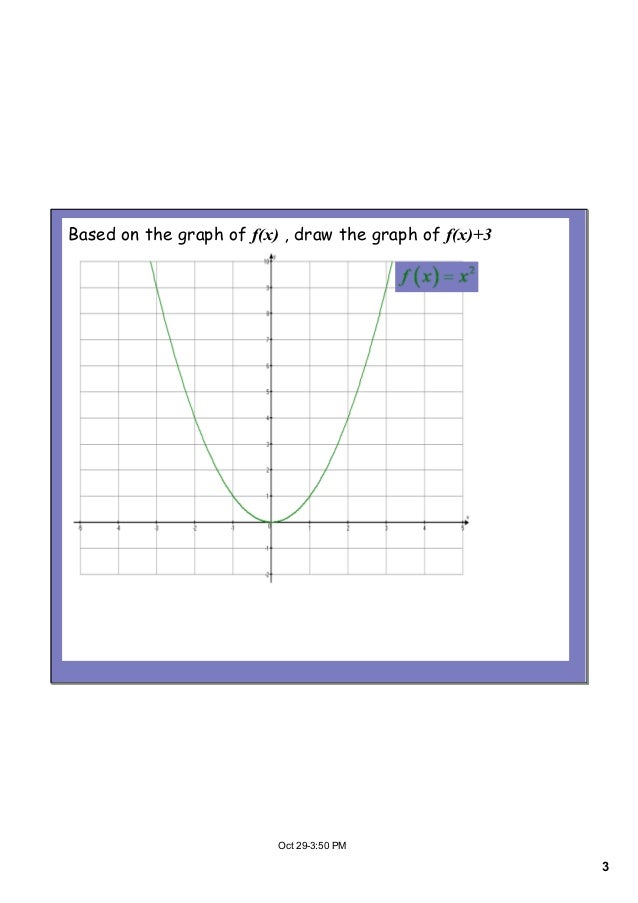



Transformations
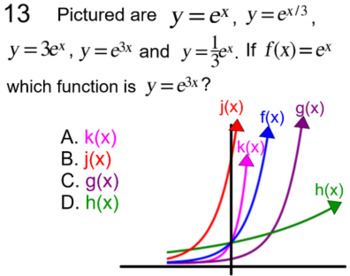



Transformations Of Functions Intro Study Aides 8 Assignments For Power Point
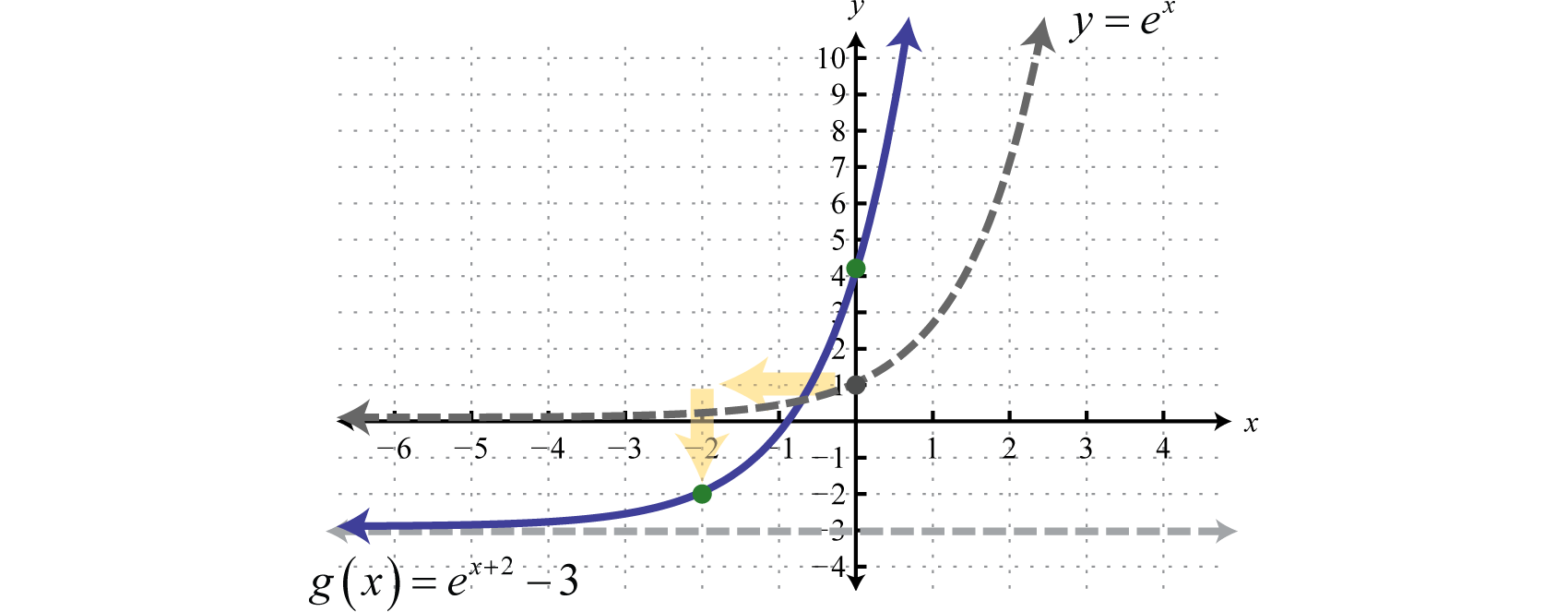



Exponential Functions And Their Graphs



コメント
コメントを投稿